前两个笔记笔者集中探讨了卷积神经网络中的卷积原理,对于二维卷积和三维卷积的原理进行了深入的剖析,对 CNN 的卷积、池化、全连接、滤波器、感受野等关键概念进行了充分的理解。本节内容将继续秉承之前 DNN 的学习路线,在利用 Tensorflow 搭建神经网络之前,先尝试利用 numpy 手动搭建卷积神经网络,以期对卷积神经网络的卷积机制、前向传播和反向传播的原理和过程有更深刻的理解。
单步卷积过程
在正式搭建 CNN 之前,我们先依据前面笔记提到的卷积机制的线性计算的理解,利用 numpy 定义一个单步卷积过程。代码如下:
def conv_single_step(a_slice_prev, W, b):
s = a_slice_prev * W # Sum over all entries of the volume s.
Z = np.sum(s) # Add bias b to Z. Cast b to a float() so that Z results in a scalar value.
Z = float(Z + b)
return Z在上述的单步卷积定义中,我们传入了一个前一层输入的要进行卷积的区域,即感受野 a_slice_prev ,滤波器 W,即卷积层的权重参数,偏差 b,对其执行 Z=Wx+b 的线性计算即可实现一个单步的卷积过程。
CNN前向传播过程:卷积
正如 DNN 中一样,CNN 即使多了卷积和池化过程,模型仍然是前向传播和反向传播的训练过程。CNN 的前向传播包括卷积和池化两个过程,我们先来看如何利用 numpy 基于上面定义的单步卷积实现完整的卷积过程。卷积计算并不难,我们在单步卷积中就已经实现了,难点在于如何实现滤波器在输入图像矩阵上的的扫描和移动过程。
这其中我们需要搞清楚一些变量和参数,以及每一个输入输出的 shape,这对于我们执行卷积和矩阵相乘至关重要。首先我们的输入是原始图像矩阵,也可以是前一层经过激活后的图像输出矩阵,这里以前一层的激活输出为准,输入像素的 shape 我们必须明确,然后是滤波器矩阵和偏差,还需要考虑步幅和填充,在此基础上我们基于滤波器移动和单步卷积搭建定义如下前向卷积过程:
def conv_forward(A_prev, W, b, hparameters):
"""
Arguments:
A_prev -- output activations of the previous layer, numpy array of shape (m, n_H_prev, n_W_prev, n_C_prev)
W -- Weights, numpy array of shape (f, f, n_C_prev, n_C)
b -- Biases, numpy array of shape (1, 1, 1, n_C)
hparameters -- python dictionary containing "stride" and "pad"
Returns:
Z -- conv output, numpy array of shape (m, n_H, n_W, n_C)
cache -- cache of values needed for the conv_backward() function
"""
# 前一层输入的shape
(m, n_H_prev, n_W_prev, n_C_prev) = A_prev.shape
# 滤波器权重的shape
(f, f, n_C_prev, n_C) = W.shape
# 步幅参数
stride = hparameters['stride']
# 填充参数
pad = hparameters['pad']
# 计算输出图像的高宽
n_H = int((n_H_prev + 2 * pad - f) / stride + 1)
n_W = int((n_W_prev + 2 * pad - f) / stride + 1)
# 初始化输出
Z = np.zeros((m, n_H, n_W, n_C))
# 对输入执行边缘填充
A_prev_pad = zero_pad(A_prev, pad)
for i in range(m):
a_prev_pad = A_prev_pad[i, :, :, :]
for h in range(n_H):
for w in range(n_W):
for c in range(n_C):
# 滤波器在输入图像上扫描
vert_start = h * stride
vert_end = vert_start + f
horiz_start = w * stride
horiz_end = horiz_start + f
# 定义感受野
a_slice_prev = a_prev_pad[vert_start : vert_end, horiz_start : horiz_end, :] # 对感受野执行单步卷积
Z[i, h, w, c] = conv_single_step(a_slice_prev, W[:,:,:,c], b[:,:,:,c])
assert(Z.shape == (m, n_H, n_W, n_C))
cache = (A_prev, W, b, hparameters)
return Z, cache这样,卷积神经网络前向传播中一个完整的卷积计算过程就被我们定义好了。通常而言,我们也会对卷积后输出加一个 relu 激活操作,正如前面的图2所示,这里我们就省略不加了。
CNN前向传播过程:池化
池化简单而言就是取局部区域最大值,池化的前向传播跟卷积过程类似,但相对简单一点,无需执行单步卷积那样的乘积运算。同样需要注意的是各参数和输入输出的 shape,因此我们定义如下前向传播池化过程:
def pool_forward(A_prev, hparameters, mode = "max"):
"""
Arguments:
A_prev -- Input data, numpy array of shape (m, n_H_prev, n_W_prev, n_C_prev)
hparameters -- python dictionary containing "f" and "stride"
mode -- the pooling mode you would like to use, defined as a string ("max" or "average")
Returns:
A -- output of the pool layer, a numpy array of shape (m, n_H, n_W, n_C)
cache -- cache used in the backward pass of the pooling layer, contains the input and hparameters
"""
# 前一层输入的shape
(m, n_H_prev, n_W_prev, n_C_prev) = A_prev.shape
# 步幅和权重参数
f = hparameters["f"]
stride = hparameters["stride"]
# 计算输出图像的高宽
n_H = int(1 + (n_H_prev - f) / stride)
n_W = int(1 + (n_W_prev - f) / stride)
n_C = n_C_prev
# 初始化输出
A = np.zeros((m, n_H, n_W, n_C))
for i in range(m):
for h in range(n_H):
for w in range(n_W):
for c in range (n_C):
# 树池在输入图像上扫描
vert_start = h * stride
vert_end = vert_start + f
horiz_start = w * stride
horiz_end = horiz_start + f
# 定义池化区域
a_prev_slice = A_prev[i, vert_start:vert_end, horiz_start:horiz_end, c]
# 选择池化类型
if mode == "max":
A[i, h, w, c] = np.max(a_prev_slice)
elif mode == "average":
A[i, h, w, c] = np.mean(a_prev_slice)
cache = (A_prev, hparameters)
assert(A.shape == (m, n_H, n_W, n_C))
return A, cache由上述代码结构可以看出,前向传播的池化过程的代码结构和卷积过程非常类似。
CNN反向传播过程:卷积
定义好前向传播之后,难点和关键点就在于如何给卷积和池化过程定义反向传播过程。卷积层的反向传播向来是个复杂的过程,Tensorflow 中我们只要定义好前向传播过程,反向传播会自动进行计算。但利用 numpy 搭建 CNN 反向传播就还得我们自己定义了。其关键还是在于准确的定义损失函数对于各个变量的梯度:
由上述梯度计算公式和卷积的前向传播过程,我们定义如下卷积的反向传播函数:
def conv_backward(dZ, cache): """
Arguments:
dZ -- gradient of the cost with respect to the output of the conv layer (Z), numpy array of shape (m, n_H, n_W, n_C)
cache -- cache of values needed for the conv_backward(), output of conv_forward()
Returns:
dA_prev -- gradient of the cost with respect to the input of the conv layer (A_prev),
numpy array of shape (m, n_H_prev, n_W_prev, n_C_prev)
dW -- gradient of the cost with respect to the weights of the conv layer (W)
numpy array of shape (f, f, n_C_prev, n_C)
db -- gradient of the cost with respect to the biases of the conv layer (b)
numpy array of shape (1, 1, 1, n_C)
"""
# 获取前向传播中存储的cache
(A_prev, W, b, hparameters) = cache
# 前一层输入的shape
(m, n_H_prev, n_W_prev, n_C_prev) = A_prev.shape
# 滤波器的 shape
(f, f, n_C_prev, n_C) = W.shape
# 步幅和权重参数
stride = hparameters['stride']
pad = hparameters['pad']
# dZ 的shape
(m, n_H, n_W, n_C) = dZ.shape
# 初始化 dA_prev, dW, db
dA_prev = np.zeros((m, n_H_prev, n_W_prev, n_C_prev))
dW = np.zeros((f, f, n_C_prev, n_C))
db = np.zeros((1, 1, 1, n_C))
# 对A_prev 和 dA_prev 执行零填充
A_prev_pad = zero_pad(A_prev, pad)
dA_prev_pad = zero_pad(dA_prev, pad)
for i in range(m):
# select ith training example from A_prev_pad and dA_prev_pad
a_prev_pad = A_prev_pad[i,:,:,:]
da_prev_pad = dA_prev_pad[i,:,:,:]
for h in range(n_H):
for w in range(n_W):
for c in range(n_C):
# 获取当前感受野
vert_start = h * stride
vert_end = vert_start + f
horiz_start = w * stride
horiz_end = horiz_start + f
# 获取当前滤波器矩阵
a_slice = a_prev_pad[vert_start:vert_end, horiz_start:horiz_end, :]
# 梯度更新
da_prev_pad[vert_start:vert_end, horiz_start:horiz_end, :] += W[:,:,:,c] * dZ[i, h, w, c]
dW[:,:,:,c] += a_slice * dZ[i, h, w, c]
db[:,:,:,c] += dZ[i, h, w, c]
dA_prev[i, :, :, :] = da_prev_pad[pad:-pad, pad:-pad, :]
assert(dA_prev.shape == (m, n_H_prev, n_W_prev, n_C_prev))
return dA_prev, dW, dbCNN反向传播过程:池化
反向传播中的池化操作跟卷积也是类似的。再此之前,我们需要根据滤波器为最大池化和平均池化分别创建一个 mask 和一个 distribute_value :
def create_mask_from_window(x):
"""
Creates a mask from an input matrix x, to identify the max entry of x.
Arguments:
x -- Array of shape (f, f)
Returns:
mask -- Array of the same shape as window, contains a True at the position corresponding to the max entry of x.
"""
mask = (x == np.max(x))
return maskdef distribute_value(dz, shape):
"""
Distributes the input value in the matrix of dimension shape
Arguments:
dz -- input scalar
shape -- the shape (n_H, n_W) of the output matrix for which we want to distribute the value of dz
Returns:
a -- Array of size (n_H, n_W) for which we distributed the value of dz
"""
(n_H, n_W) = shape
# Compute the value to distribute on the matrix
average = dz / (n_H * n_W)
# Create a matrix where every entry is the "average" value
a = np.full(shape, average)
return a然后整合封装最大池化的反向传播过程:
def pool_backward(dA, cache, mode = "max"):
"""
Arguments:
dA -- gradient of cost with respect to the output of the pooling layer, same shape as A
cache -- cache output from the forward pass of the pooling layer, contains the layer's input and hparameters
mode -- the pooling mode you would like to use, defined as a string ("max" or "average")
Returns:
dA_prev -- gradient of cost with respect to the input of the pooling layer, same shape as A_prev
"""
# Retrieve information from cache
(A_prev, hparameters) = cache
# Retrieve hyperparameters from "hparameters"
stride = hparameters['stride']
f = hparameters['f']
# Retrieve dimensions from A_prev's shape and dA's shape
m, n_H_prev, n_W_prev, n_C_prev = A_prev.shape
m, n_H, n_W, n_C = dA.shape
# Initialize dA_prev with zeros
dA_prev = np.zeros((m, n_H_prev, n_W_prev, n_C_prev))
for i in range(m):
# select training example from A_prev
a_prev = A_prev[i,:,:,:]
for h in range(n_H):
for w in range(n_W):
for c in range(n_C):
# Find the corners of the current "slice"
vert_start = h * stride
vert_end = vert_start + f
horiz_start = w * stride
horiz_end = horiz_start + f
# Compute the backward propagation in both modes.
if mode == "max":
a_prev_slice = a_prev[vert_start:vert_end, horiz_start:horiz_end, c]
mask = create_mask_from_window(a_prev_slice)
dA_prev[i, vert_start: vert_end, horiz_start: horiz_end, c] += np.multiply(mask, dA[i,h,w,c]) elif mode == "average": # Get the value a from dA
da = dA[i,h,w,c]
# Define the shape of the filter as fxf
shape = (f,f)
# Distribute it to get the correct slice of dA_prev. i.e. Add the distributed value of da.
dA_prev[i, vert_start: vert_end, horiz_start: horiz_end, c] += distribute_value(da, shape)
# Making sure your output shape is correct
assert(dA_prev.shape == A_prev.shape)
return dA_prev这样卷积神经网络的整个前向传播和反向传播过程我们就搭建好了。可以说是非常费力的操作了,但我相信,经过这样一步步的根据原理的手写,你一定会对卷积神经网络的原理理解更加深刻了。
本文由《自兴动脑人工智能》项目部 凯文 投稿。
-
神经网络
+关注
关注
42文章
4829浏览量
106891 -
人工智能
+关注
关注
1813文章
49785浏览量
261924 -
机器学习
+关注
关注
66文章
8541浏览量
136283 -
深度学习
+关注
关注
73文章
5591浏览量
123971
发布评论请先 登录
CNN卷积神经网络设计原理及在MCU200T上仿真测试
NMSIS神经网络库使用介绍
构建CNN网络模型并优化的一般化建议
从零开始利用NMSIS库搭建神经网络(一)
在Ubuntu20.04系统中训练神经网络模型的一些经验
CICC2033神经网络部署相关操作
基于FPGA搭建神经网络的步骤解析





 【连载】深度学习笔记11:利用numpy搭建一个卷积神经网络
【连载】深度学习笔记11:利用numpy搭建一个卷积神经网络


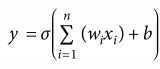










评论