关键字:ATTINY85,电子蜡烛电路
想想当你好不容易跟女朋友共度烛光晚餐,却因为蜡烛点没了或打翻着火了,那是一件多么坑爹的事啊!今天为你分享一款自己diy的超自然的烛光蜡烛。
ATtiny 电子蜡烛,皮特•米尔斯开发这个伟大的蜡烛,正如我们图片所见到的一样,但怎样让这蜡烛的光芒像传统的蜡烛一样闪烁呢。
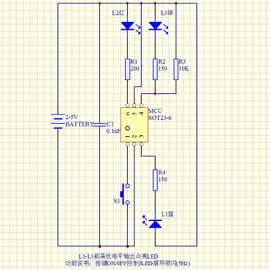
ATtiny 电子蜡烛最难的部分就闪烁神态逼真,所以皮特做了一个蜡烛光检测电阻( LDR )和固定电阻作为一个分压器。这是作为ATTINY85 ADC之中的一个输入端,并离散时间间隔的进行采样。采样速率为100毫秒。然后将采集的8bit的电频值存储到EEPROM中,以便记录蜡烛的闪烁图谱,驱动将其连接的LED、PWM形成通路。在用三节干电池供电。最后您只需编程程序,然后通过开关进行控制。
下面是ATtiny 电子蜡烛的电路图
下面是程序的代码以及写入EEPROM的数据
view plainprint? /* Program Description: This program reads a light detecting resistor thru an internal ADC and stores the value, after scaling it, to eeprom. This ADC value is sent to a PWM channel with attached led. This is essentially a data logger for light and replay by LED. If, if you aim the LDR at a flickering candle during its recording phase, you have a flickering led candle. A circuit description and other details can be found at http://petemills.blogspot.com Filename: ATTiny_Candle_v1.0.c Author: Pete Mills Int. RC Osc. 8 MHz; Start-up time PWRDWN/RESET: 6 CK/14 CK + 64 ms */ //********** Includes ********** #include #include#include //********** Definitions ********** // LED for flame simulation #define LED PB0 #define LED_PORT PORTB #define LED_DDR DDRB // Light Detecting Resistor for recording a live flame #define LDR PINB3 #define LDR_PORT PINB #define LDR_DDR DDRB // Tactile Switch Input #define SW1 PINB4 #define SW1_PORT PINB #define SW1_DDR DDRB #define ARRAY_SIZE 500 // size of the flicker array #define SAMPLE_RATE 100 // ms delay for collecting and reproducing the flicker //********** Function Prototypes ********** void setup(void); void toggle_led(void); void program_flicker(void); void led_alert(void); void eeprom_save_array(void); void eeprom_read_array(void); void scale_array(void); uint8_t get_adc(void); uint8_t scale( uint8_t input, uint8_t inp_low, uint8_t inp_hi, uint8_t outp_low, uint8_t outp_hi); uint8_t is_input_low(char port, char channel, uint8_t debounce_time, int input_block); //********** Global Variables ********** uint8_t flicker_array[ ARRAY_SIZE ] = { 0 }; uint8_t EEMEM ee_flicker_array[ ARRAY_SIZE ] = { 0 }; int main(void) { uint16_t replay = 0; setup(); eeprom_read_array(); while(1) { if( is_input_low( SW1_PORT, SW1, 25, 250 ) ) { // program the flicker // after entering and upon completion, a predetermined flash pattern will occur as described in led_alert() // aim the ldr at a flickering candle or any other light source ( like a laser ) you want to record during this time // and upon completion the values are stored to eeprom. They are played back immediately as well // as being recalled from eeprom upon first start up led_alert(); program_flicker(); scale_array(); eeprom_save_array(); led_alert(); } // replay the recorded flicker pattern OCR0A = flicker_array[ replay ]; ++replay; if( replay >= ( ARRAY_SIZE - 13 ) ) // if the end of the stored array has been reached { replay = 0; // start again from the beginning //led_alert(); } _delay_ms( SAMPLE_RATE ); _delay_ms( 3 ); // ADC Conversion time } } //********** Functions ********** void setup(void) { //********* Port Config ********* LED_DDR |= ( 1 << LED); // set PB0 to "1" for output LED_PORT &= ~( 1 << LED ); // turn the led off LDR_DDR &= ~( 1 << LDR ); // set LDR pin to 0 for input LDR_PORT |= ( 1 << LDR ); // write 1 to enable internal pullup SW1_DDR &= ~( 1 << SW1 ); // set sw1 pin to 0 for input SW1_PORT |= ( 1 << SW1 ); // write a 1 to sw1 to enable the internal pullup //********** PWM Config ********* TCCR0A |= ( ( 1 << COM0A1 ) | ( 1 << WGM01 ) | ( 1 << WGM00 ) ); // non inverting fast pwm TCCR0B |= ( 1 << CS00 ); // start the timer //********** ADC Config ********** ADMUX |= ( ( 1 << ADLAR ) | ( 1 << MUX1 ) | ( 1 << MUX0 ) ); // left adjust and select ADC3 ADCSRA |= ( ( 1 << ADEN ) | ( 1 << ADPS2 ) | ( 1 << ADPS1 ) ); // ADC enable and clock divide 8MHz by 64 for 125khz sample rate DIDR0 |= ( 1 << ADC3D ); // disable digital input on analog input channel to conserve power } void toggle_led() { LED_PORT ^= ( 1 << LED ); } uint8_t is_input_low( char port, char channel, uint8_t debounce_time, int input_block ) { /* This function is for debouncing a switch input Debounce time is a blocking interval to wait until the input is tested again. If the input tests low again, a delay equal to input_block is executed and the function returns ( 1 ) */ if ( bit_is_clear( port, channel ) ) { _delay_ms( debounce_time ); if ( bit_is_clear( port, channel ) ) { _delay_ms( input_block ); return 1; } } return 0; } uint8_t get_adc() { ADCSRA |= ( 1 << ADSC ); // start the ADC Conversion while( ADCSRA & ( 1 << ADSC )); // wait for the conversion to be complete return ~ADCH; // return the inverted 8-bit left adjusted adc val } void program_flicker() { // build the flicker array for( int i = 0; i < ARRAY_SIZE; i++ ) { flicker_array[ i ] = get_adc(); _delay_ms( SAMPLE_RATE ); } } void led_alert() { // this is a function to create a visual alert that an event has occured within the program // it toggles the led 10 times. for( int i = 0; i < 10; i++ ) { OCR0A = 0; _delay_ms( 40 ); OCR0A = 255; _delay_ms( 40 ); } } void eeprom_save_array() { for( int i = 0; i < ARRAY_SIZE; i++ ) { eeprom_write_byte( &ee_flicker_array[ i ], flicker_array[ i ] ); } } void eeprom_read_array() { for( int i = 0; i < ARRAY_SIZE; i++ ) { flicker_array[ i ] = eeprom_read_byte( &ee_flicker_array[ i ] ); } } uint8_t scale( uint8_t input, uint8_t inp_low, uint8_t inp_hi, uint8_t outp_low, uint8_t outp_hi) { return ( ( ( input - inp_low ) * ( outp_hi - outp_low ) ) / ( ( inp_hi - inp_low ) + outp_low ) ); } void scale_array() { uint8_t arr_min = 255; uint8_t arr_max = 0; uint8_t out_low = 20; uint8_t out_high = 255; // find the min and max values for( int i = 0; i < ARRAY_SIZE; i++ ) { if( flicker_array[ i ] < arr_min ) arr_min = flicker_array[ i ]; if( flicker_array[ i ] > arr_max ) arr_max = flicker_array[ i ]; } // now that we know the range, scale it for( int i = 0; i < ARRAY_SIZE; i++ ) { flicker_array[ i ] = scale( flicker_array[ i ], arr_min, arr_max, out_low, out_high ); } } igh ); } } igh ); } } } } } } } } } } } } } }
EEPROM的数据
rom.rar
声明:本文内容及配图由入驻作者撰写或者入驻合作网站授权转载。文章观点仅代表作者本人,不代表电子发烧友网立场。文章及其配图仅供工程师学习之用,如有内容侵权或者其他违规问题,请联系本站处理。
举报投诉
发布评论请先 登录
相关推荐
热点推荐
广州唯创电子单片机语音芯片:智能设备的声音灵魂与技术核心
。单片机(MicrocontrollerUnit,MCU)是集成处理器、存储器和多种外围接口的微型计算机系统。它以其高度集成、低功耗、强控制能力等特点,成为现代电子

单片机电路设计必读:电容选用的五大关键原则
表现。电容在单片机电路中的核心作用单片机的稳定运行离不开电容的保驾护航。去耦电容用于消除电源噪声,耦合电容负责信号传输,起振电容确保时钟精准,复位电容保障系统启动可靠。这些看似简单的

ATtiny3224/3226/3227:高性能低功耗的tinyAVR® 2系列微控制器
Microchip Technology ATtiny3224、ATtiny3226与ATtiny3227 8位微控制器 (MCU) 采用带硬件乘法器的AVR® CPU,运行速率高达20MHz,具有

怎么测单片机系统频率
单片机系统频率是指单片机工作时的时钟频率,它直接影响单片机的运行速度和处理能力,准确测量系统频率对单片机应用开发、程序调试和性能优化具有重要意义。测量
单片机怎么驱动电机?
在各类自动化设备和智能装置中,电机是重要的执行部件,而单片机作为控制核心,需要通过特定的方式驱动电机运转。单片机驱动电机并非直接连接即可,而是要根据电机类型和功率,搭配合适的驱动电路,才能实现稳定
单片机怎么烧程序
单片机烧程序是将编写好的程序代码写入单片机内部存储单元,让单片机按照预设逻辑工作的过程,是单片机应用开发中不可或缺的环节。无论是简单的灯光控制程序,还是复杂的工业控制算法,都需要通过烧
单片机定制开发的设计思路
。开发团队需与客户充分沟通,明确设备的应用场景、功能目标、性能指标以及成本预算等。例如,在工业控制设备中,单片机可能需要具备较强的抗干扰能力和实时数据处理功能;而在消费电子领域,低功耗和小型化往往是重点考量因素
单片机科普总结,建议收藏!
单片机(MicrocontrollerUnit,MCU)作为嵌入式系统的核心之一,在现代电子产品中无处不在。从智能家居、汽车电子,到工业控制、医疗设备,单片机支撑着无数智能化应用的发展

stm32L0单片机电源管脚对地电阻异常是什么原因导致的?
部分stm32L0单片机电源管脚对地电阻异常,有的200欧姆左右,有的500欧姆左右。导致功耗变大,什么原因会导致电源管脚对地电阻变低异常。
发表于 03-07 07:19
单片机中断技术详解
在现代电子设备中,单片机作为控制核心发挥着举足轻重的作用。而在其高效运作的背后,中断机制是推动单片机实现实时响应与高效执行的关键因素。本文将深入探讨单片机中的中断概念、中断系统的结构、
单片机在电子技术中的应用及发展
单片机作为一种高度集成的微控制器,在电子技术领域有着广泛的应用。本文首先介绍了单片机在多个领域的具体应用,包括自动化仪器仪表、家用电器、医用设备、通信设备、汽车电子控制与检测以及模块化
单片机Debug工具性能对比 单片机调试常用命令
单片机(Microcontroller Unit, MCU)调试是嵌入式开发中的一个重要环节,它帮助开发者发现和修复代码中的错误,优化程序性能。不同的单片机和开发环境可能使用不同的调试工具和命令





 ATtiny单片机电子蜡烛,ATtiny candle
ATtiny单片机电子蜡烛,ATtiny candle











评论