Linux内核中,有许许多多的精妙设计,比如在内核代码中,运用到了大量的【链表】这种数据结构,而在Linux内核中,针对如此多的链表要进行操作,他们分别是如何定义和管理的呢?本文将给你展示,Linux内核中list.h的高效应用。
在上一篇文章中,我们已经介绍过了lish.h在 单向链表 中的应用,本文乘胜追击,再次介绍一下lish.h在 双向链表 中的应用。
通过本文的阅读,你将了解到以下内容:
- list.h的全貌(上篇文章已经介绍过了)
- 如何使用list.h创建双向链表并实现链表的基本操作?
如何使用list.h创建双向链表并实现链表的基本操作?
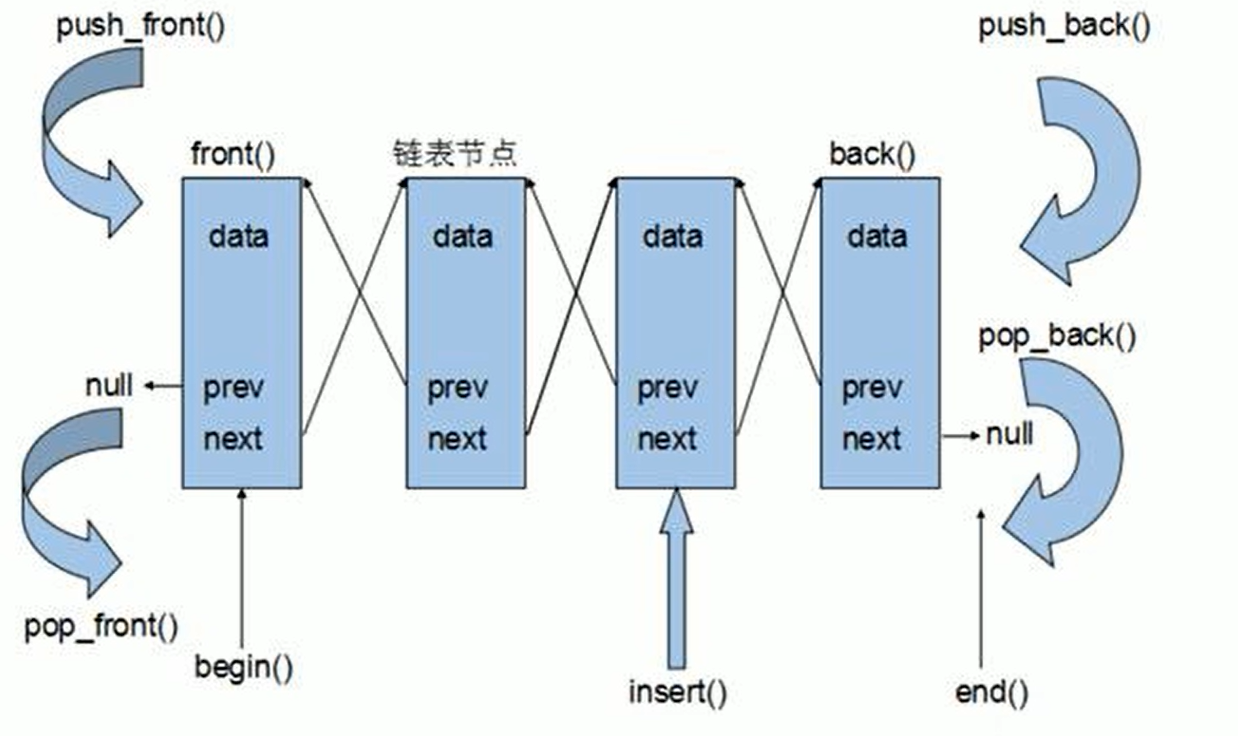
单向链表与双向链表的最大区别就是:双向链表可以同时从表头和表尾操作,即【双向】。我们将上面单向链表的实现代码,稍微改改,配合list.h提供的接口,即可实现双向链表的基本操作。示例代码如下:
/******************************************************************
本文件借助linux_list.h实现【双向链表】的基本操作:
创建、添加、查找、修改、删除、销毁、打印等
******************************************************************/
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include "linux_list.h"
/** 查找链表的方向 */
#define LIST_FROM_HEAD_TO_TAIL 1
#define LIST_FROM_TAIL_TO_HEAD 0
/** 链表节点中存储的实际内容 */
typedef struct _data_node_t {
int index;
char msg[128];
} node_data_t;
/** 链表节点的对外数据类型定义 */
typedef struct _my_list_node_t {
node_data_t data;
struct list_head list;
} my_list_node_t ;
/** 定义链表的表头 */
static my_list_node_t g_list_head;
/** 定义链表当前的节点个数 */
static int g_list_node_cnt = 0;
/** 链表创建 */
int my_list_create(void)
{
INIT_LIST_HEAD(&g_list_head.list);
return 0;
}
/** 链表增加节点到链表尾部 */
int my_list_add_tail_node(const node_data_t *data)
{
my_list_node_t *node;
node = (my_list_node_t *)malloc(sizeof(my_list_node_t));
if (!node) {
printf("memory error !\n");
return -1;
}
node->data.index = data->index;
snprintf(node->data.msg, sizeof(node->data.msg), "%s", data->msg);
list_add_tail(&node->list, &g_list_head.list);
g_list_node_cnt ++;
return 0;
}
/** 链表增加节点到链表头部 */
int my_list_add_head_node(const node_data_t *data)
{
my_list_node_t *node;
node = (my_list_node_t *)malloc(sizeof(my_list_node_t));
if (!node) {
printf("memory error !\n");
return -1;
}
node->data.index = data->index;
snprintf(node->data.msg, sizeof(node->data.msg), "%s", data->msg);
list_add(&node->list, &g_list_head.list);
g_list_node_cnt ++;
return 0;
}
/** 链表查找节点(从头往尾查找) */
my_list_node_t * my_list_query_node_from_head(const node_data_t *data)
{
struct list_head *pos,*n;
my_list_node_t *p;
list_for_each_safe(pos, n, &g_list_head.list)
{
p = list_entry(pos, my_list_node_t, list);
if((p->data.index == data->index) && (!strcmp((char*)p->data.msg, data->msg)))
{
//printf("found index=%d, msg=%s\n", data->index, data->msg);
return p;
}
}
return NULL;
}
/** 链表查找节点(从尾往头查找) */
my_list_node_t * my_list_query_node_from_tail(const node_data_t *data)
{
struct list_head *pos,*n;
my_list_node_t *p;
list_for_each_prev_safe(pos, n, &g_list_head.list)
{
p = list_entry(pos, my_list_node_t, list);
if((p->data.index == data->index) && (!strcmp((char*)p->data.msg, data->msg)))
{
//printf("found index=%d, msg=%s\n", data->index, data->msg);
return p;
}
}
return NULL;
}
/** 链表查找节点(dir, 为1表示从头往尾查找, 为0表示从尾往头查找) */
my_list_node_t * my_list_query_node(const node_data_t *data, int dir)
{
if (dir) {
return my_list_query_node_from_head(data);
} else {
return my_list_query_node_from_tail(data);
}
}
/** 链表将一个节点的内容进行修改 */
int my_list_modify_node(const node_data_t *old_data, const node_data_t *new_data)
{
my_list_node_t *p = my_list_query_node(old_data, LIST_FROM_HEAD_TO_TAIL);
if (p)
{
p->data.index = new_data->index;
snprintf(p->data.msg, sizeof(p->data.msg), "%s", new_data->msg);
return 0;
}
else
{
printf("Node index=%d, msg=%s, not found !\n", old_data->index, old_data->msg);
return -1;
}
}
/** 链表删除一个节点 */
int my_list_delete_node(const node_data_t *data)
{
my_list_node_t *p = my_list_query_node(data, LIST_FROM_HEAD_TO_TAIL); //默认从头部开始查找节点
if (p)
{
struct list_head *pos = &p->list;
list_del(pos);
free(p);
g_list_node_cnt --;
return 0;
}
else
{
printf("Node index=%d, msg=%s, not found !\n", data->index, data->msg);
return -1;
}
}
/** 链表删除所有节点 */
int my_list_delete_all_node(void)
{
struct list_head *pos,*n;
my_list_node_t *p;
list_for_each_safe(pos, n, &g_list_head.list)
{
p = list_entry(pos, my_list_node_t, list);
list_del(pos);
free(p);
}
g_list_node_cnt = 0;
return 0;
}
/** 链表销毁 */
int my_list_destory(void)
{
/** do nothing here ! */
return 0;
}
/** 链表内容打印 */
int my_list_print(int print_index)
{
int i = 1;
struct list_head * pos,*n;
my_list_node_t * node;
printf("==================== %d ===========================\n", print_index);
printf("cur list data : g_list_node_cnt = %d \n", g_list_node_cnt);
list_for_each_safe(pos, n, &g_list_head.list) //调用linux_list.h中的list_for_each函数进行遍历
{
node = list_entry(pos, my_list_node_t, list); //调用list_entry函数得到相对应的节点
printf("Node %2d's : index=%-3d, msg=%-20s\n",
i++, node->data.index, node->data.msg);
}
printf("==================================================\n");
return 0;
}
int main(int argc, const char *argv[])
{
int retval = -1;
my_list_node_t *p;
const node_data_t data1 = {1, "a1bcde"};
const node_data_t data2 = {2, "ab2cde"};
const node_data_t data3 = {3, "abc3de"};
const node_data_t data4 = {4, "abcd4e"};
const node_data_t data5 = {5, "abcde5"};
const node_data_t data6 = {6, "abcde5666"}; // 定义一个不添加到链表的节点信息
const node_data_t data7 = {7, "abcde5777"}; // 定义一个被修改的节点信息
const node_data_t data8 = {8, "abcde5888"}; // 定义一个修改后的节点信息
/** 创建一个空链表 */
retval = my_list_create();
if (!retval) {
printf("list create ok !!!\n");
}
printf("\n\n\n");
/** 往链表的尾部添加6个节点 */
retval = my_list_add_head_node(&data1);
if (!retval) {
printf("node1 add ok !\n");
}
retval = my_list_add_tail_node(&data2);
if (!retval) {
printf("node2 add ok !\n");
}
retval = my_list_add_head_node(&data3);
if (!retval) {
printf("node3 add ok !\n");
}
retval = my_list_add_tail_node(&data4);
if (!retval) {
printf("node4 add ok !\n");
}
retval = my_list_add_head_node(&data5);
if (!retval) {
printf("node5 add ok !\n");
}
retval = my_list_add_tail_node(&data7);
if (!retval) {
printf("node7 add ok !\n");
}
printf("\n\n\n");
/** 分别查询刚刚添加的前5个节点 */
p = my_list_query_node(&data1, LIST_FROM_HEAD_TO_TAIL);
if (p) {
printf("node %d,%s, found !!!\n", data1.index, data1.msg);
}
p = my_list_query_node(&data2, LIST_FROM_TAIL_TO_HEAD);
if (p) {
printf("node %d,%s, found !!!\n", data2.index, data2.msg);
}
p = my_list_query_node(&data3, LIST_FROM_HEAD_TO_TAIL);
if (p) {
printf("node %d,%s, found !!!\n", data3.index, data3.msg);
}
p = my_list_query_node(&data4, LIST_FROM_TAIL_TO_HEAD);
if (p) {
printf("node %d,%s, found !!!\n", data4.index, data4.msg);
}
p = my_list_query_node(&data5, LIST_FROM_HEAD_TO_TAIL);
if (p) {
printf("node %d,%s, found !!!\n", data5.index, data5.msg);
}
/** 查询一个没有添加到链表中的节点,即不存在的节点 */
p = my_list_query_node(&data6, LIST_FROM_HEAD_TO_TAIL);
if (!p) {
printf("node %d,%s, found fail !!!\n", data6.index, data6.msg);
}
p = my_list_query_node(&data6, LIST_FROM_TAIL_TO_HEAD);
if (!p) {
printf("node %d,%s, found fail !!!\n", data6.index, data6.msg);
}
/** 打印当前链表的节点信息 */
printf("\n\n\n");
my_list_print(1);
printf("\n\n\n");
/** 将data7的信息修改为data8的内容 */
retval = my_list_modify_node(&data7, &data8);
if (!retval) {
printf("node %d,%s => %d,%s, modify ok !!!\n", data7.index, data7.msg, data8.index, data8.msg);
} else {
printf("node %d,%s => %d,%s, modify fail !!!\n", data7.index, data7.msg, data8.index, data8.msg);
}
/** 查询刚刚被修改了的节点data7,即不存在的节点 */
p = my_list_query_node(&data7, LIST_FROM_HEAD_TO_TAIL);
if (!p) {
printf("node %d,%s, found fail !!!\n", data7.index, data7.msg);
}
/** 查询刚刚被修改后的节点data8,即存在的节点 */
p = my_list_query_node(&data8, LIST_FROM_TAIL_TO_HEAD);
if (p) {
printf("node %d,%s, found ok !!!\n", data8.index, data8.msg);
}
/** 打印当前链表的节点信息 */
printf("\n\n\n");
my_list_print(2);
printf("\n\n\n");
/** 删除一个存在于链表中的节点 */
retval = my_list_delete_node(&data4);
if (!retval) {
printf("node %d,%s, delete ok !!!\n", data4.index, data4.msg);
}
printf("\n\n\n");
/** 再次查询刚刚已删除的节点 */
p = my_list_query_node(&data4, LIST_FROM_HEAD_TO_TAIL);
if (p) {
printf("node %d,%s, found ok !!!\n", data4.index, data4.msg);
} else {
printf("node %d,%s, found fail !!!\n", data4.index, data4.msg);
}
printf("\n\n\n");
/** 删除一个不存在于链表中的节点 */
retval = my_list_delete_node(&data6);
if (retval) {
printf("node %d,%s, delete fail !!!\n", data6.index, data6.msg);
}
/** 打印当前链表的节点信息 */
printf("\n\n\n");
my_list_print(3);
printf("\n\n\n");
/** 删除链表的所有节点 */
retval = my_list_delete_all_node();
if (!retval) {
printf("all list notes delete done !\n");
}
/** 打印当前链表的节点信息 */
printf("\n\n\n");
my_list_print(4);
printf("\n\n\n");
/** 销毁链表 */
retval = my_list_destory();
if (!retval) {
printf("list destory done !\n");
}
/** 打印当前链表的节点信息 */
printf("\n\n\n");
my_list_print(5);
printf("\n\n\n");
return retval;
}
[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-BAOzFCxb-1662955522821)(data:image/gif;base64,R0lGODlhAQABAPABAP///wAAACH5BAEKAAAALAAAAAABAAEAAAICRAEAOw==)]
在main函数中,我们使用了与单向链表一样的测试案例,运行结果如下:
root@liluchang-ubuntu:/share/llc/linux_list# ./linux_double_list
list create ok !!!
node1 add ok !
node2 add ok !
node3 add ok !
node4 add ok !
node5 add ok !
node7 add ok !
node 1,a1bcde, found !!!
node 2,ab2cde, found !!!
node 3,abc3de, found !!!
node 4,abcd4e, found !!!
node 5,abcde5, found !!!
node 6,abcde5666, found fail !!!
node 6,abcde5666, found fail !!!
==================== 1 ===========================
cur list data : g_list_node_cnt = 6
Node 1's : index=5 , msg=abcde5
Node 2's : index=3 , msg=abc3de
Node 3's : index=1 , msg=a1bcde
Node 4's : index=2 , msg=ab2cde
Node 5's : index=4 , msg=abcd4e
Node 6's : index=7 , msg=abcde5777
==================================================
node 7,abcde5777 => 8,abcde5888, modify ok !!!
node 7,abcde5777, found fail !!!
node 8,abcde5888, found ok !!!
==================== 2 ===========================
cur list data : g_list_node_cnt = 6
Node 1's : index=5 , msg=abcde5
Node 2's : index=3 , msg=abc3de
Node 3's : index=1 , msg=a1bcde
Node 4's : index=2 , msg=ab2cde
Node 5's : index=4 , msg=abcd4e
Node 6's : index=8 , msg=abcde5888
==================================================
node 4,abcd4e, delete ok !!!
node 4,abcd4e, found fail !!!
Node index=6, msg=abcde5666, not found !
node 6,abcde5666, delete fail !!!
==================== 3 ===========================
cur list data : g_list_node_cnt = 5
Node 1's : index=5 , msg=abcde5
Node 2's : index=3 , msg=abc3de
Node 3's : index=1 , msg=a1bcde
Node 4's : index=2 , msg=ab2cde
Node 5's : index=8 , msg=abcde5888
==================================================
all list notes delete done !
==================== 4 ===========================
cur list data : g_list_node_cnt = 0
==================================================
list destory done !
==================== 5 ===========================
cur list data : g_list_node_cnt = 0
==================================================
对比运行的结果,发现与单向链表的测试结果一致,证明2者的实现功能是一致。
那么在实际项目过程中,究竟使用单向链表还是双向链表呢?这就要根据具体的项目需求,灵活使用,不同的应用场景使用不同的链表实现,也许能达到事半功倍的效果。
好了,本次关于Linux内核的list.h的应用,就介绍到这里,如果有疑问,欢迎在评论席提出。感谢您的阅读。
-
Linux
+关注
关注
88文章
11628浏览量
217965 -
链表
+关注
关注
0文章
80浏览量
11000
发布评论请先 登录
Linux Kernel数据结构:链表
【HarmonyOS】双向循环链表篇
Linux内核中的数据结构的一点认识
深入浅出linux内核源代码之双向链表list_head说明文档
FreeRTOS代码剖析之5:链表管理list.c





 【Linux高级编译】list.h的高效应用—双向链表的实现
【Linux高级编译】list.h的高效应用—双向链表的实现












评论