作者简介
伟林,中年码农,从事过电信、手机、安全、芯片等行业,目前依旧从事Linux方向开发工作,个人爱好Linux相关知识分享,个人微博CSDN pwl999,欢迎大家关注!
Q学员问:我最近在看k8s对cgroup的管理部分,对于cfs对cgroup的调度有些疑惑。想搞明白cgroup里面的 period、quota是如何影响cfs的调度的
A伟林老师给出如下文章进行解答
1.Cgroup
1.1、cgroup概念
cgroup最基本的操作时我们可以使用以下命令创建一个cgroup文件夹:
mount-tcgroup-ocpu,cpusetcpu&cpuset/dev/cpu_cpuset_test
那么/dev/cpu_cpuset_test文件夹下就有一系列的cpu、cpuset cgroup相关的控制节点,tasks文件中默认加入了所有进程到这个cgroup中。可以继续创建子文件夹,子文件夹继承了父文件夹的结构形式,我们可以给子文件夹配置不同的参数,把一部分进程加入到子文件夹中的tasks文件当中,久可以实现分开的cgroup控制了。
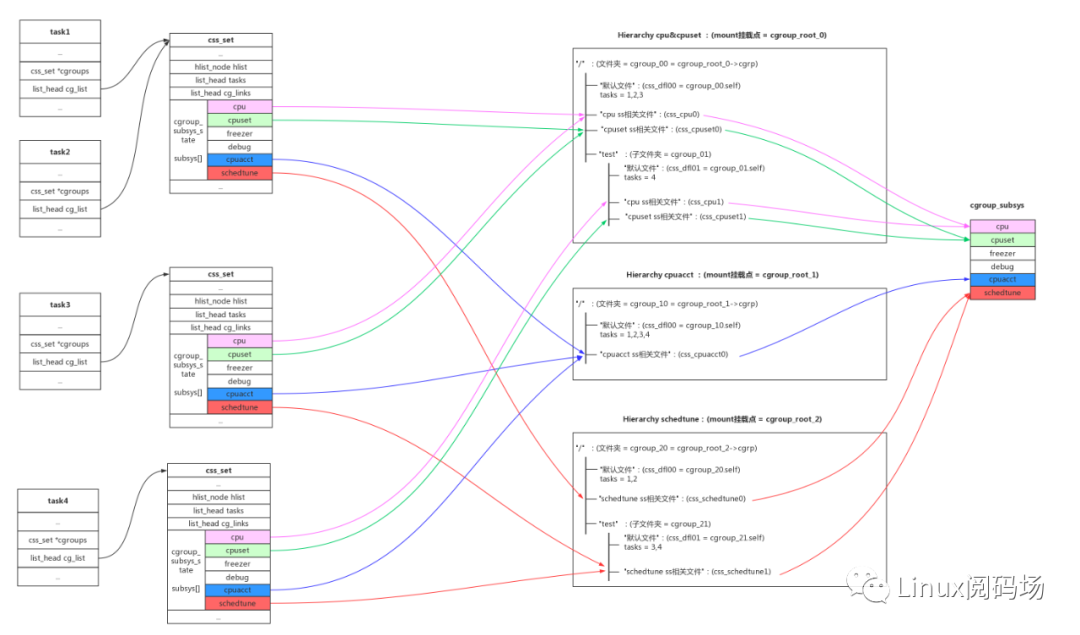
关于cgroup的结构有以下规则和规律:
-
1、cgroup有很多subsys,我们平时接触到的cpu、cpuset、cpuacct、memory、blkio都是cgroup_subsys;
-
2、一个cgroup hierarchy,就是使用mount命令挂载的一个cgroup文件系统,hierarchy对应mount的根cgroup_root;
-
3、一个hierarchy可以制定一个subsys,也可以制定多个subsys。可以是一个subsys,也可以是一个subsys组合;
-
4、一个subsys只能被一个hierarchy引用一次,如果subsys已经被hierarchy引用,新hierarchy创建时不能引用这个subsys;唯一例外的是,我们可以创建和旧的hierarchy相同的subsys组合,这其实没有创建新的hierarchy,只是简单的符号链接;
-
5、hierarchy对应一个文件系统,cgroup对应这个文件系统中的文件夹;subsys是基类,而css(cgroup_subsys_state)是cgroup引用subsys的实例;比如父目录和子目录分别是两个cgroup,他们都要引用相同的subsys,但是他们需要不同的配置,所以会创建不同的css供cgroup->subsys[]来引用;
-
6、一个任务对系统中不同的subsys一定会有引用,但是会引用到不同的hierarchy不同的cgroup即不同css当中;所以系统使用css_set结构来管理任务对css的引。如果任务引用的css组合相同,那他们开源使用相同的css_set;
-
7、还有cgroup到task的反向引用,系统引入了cg_group_link结构。这部分可以参考Docker背后的内核知识——cgroups资源限制一文的描述,如下图的结构关系:
cgroup数据结构之间的关系
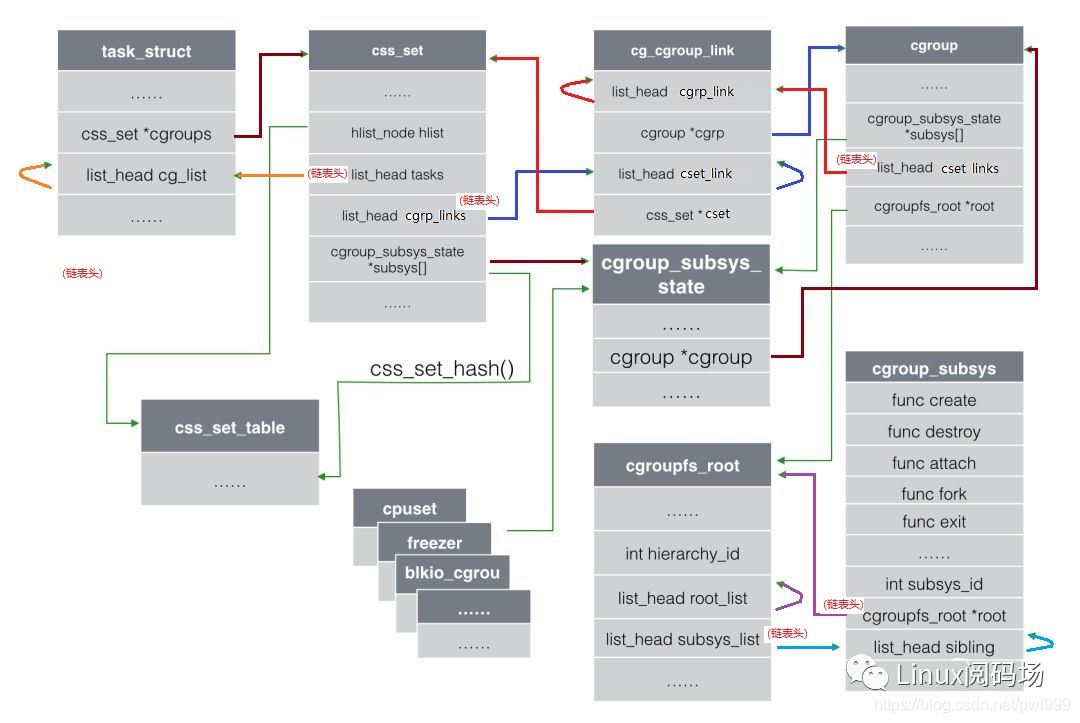
1、subsys是一组基类(cpu、blkio),css(cgroup_subsys_state)是基类的实例化。
2、cgroup的一组css的集合。
3、hierarchy是多个cgoup的组合,它决定cgroup中能创建哪些subsys的css。hierarchy可以任意引用几种subsys,但是一个subsys只能被一个hierarchy引用。如果一个hierarchy已经引用某个subsys,那么其他hierarchy就不能再引用这个subsys了。hierarchy对应cgroupfs_root数据结构。
4、一旦hierarchy确定了subsys,那么它下面的cgroup只能创建对应的css实例。一个subsys只能存在于某个hierarchy中,hierarchy下的多个cgroup可以创建这个subsys对应的多个css。
5、hierarchy、cgroup、css三者还使用文件系统来表示层次关系:hierarchy是文件系统挂载点,cgroup是文件夹,css是文件夹中的文件。css的值,以及兄弟和父子关系,表示了subsys资源配额的关系。
6、cgoup是为了划分资源配额,配置的主体是进程task。每个task在每一类别的subsys上都有配额,所以每个task在每个类别的subsys上有一个唯一的css与之关联。
7、进程和css是一对多(1 x N)的关系。而系统中的多个进程和多个css,是多对多(M x N)的关系。为了收敛这种多对多的关系,系统把所有css属性都相同的一组进程放在一个css_set当中,把多个css放在一个cgroup当中,这样还是多对多但是已经收敛(M/a x N/b)。css_set根据属性组合,存入css_set_table当中。
8、css_set代表a个css属性相同的进程,cgroup代表引用的b个subsys。多对多的关系从task vs css的(M x N),收敛到css_set vs cgroup的(M/a x N/b)。为了进一步简化css_set和cgroup之间多对多关系的双向查找,引入了cg_group_link数据结构:
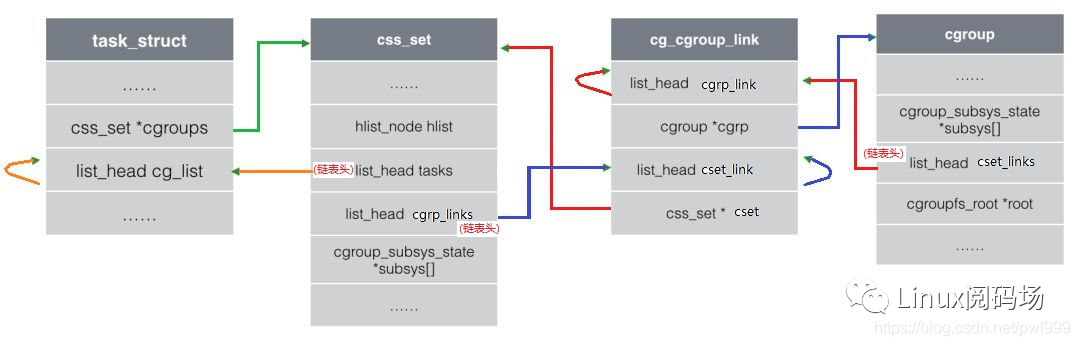
task_struct通过->cgroup成员找到css_set结构,css_set利用->tasks链表把所有css属性相同的进程链接到一起。
| dir | descript |
| css_set → cgroup | css_set的->cgrp_links链表上挂载了这组css相关cgroup对应的cg_cgroup_link,通过cg_cgroup_link->cgrp找到cgroup,再通过cgroup->subsys[]找到css。 |
| cgroup → css_set | cgroup的->cset_links链表上挂载了所有指向本cgoup的task对应的cg_cgroup_link,通过cg_cgroup_link->cset找到css_set,再通过css_set->tasks找到所有的task_struct。 |
9、还有一条task_struct → cgroup 的通路:
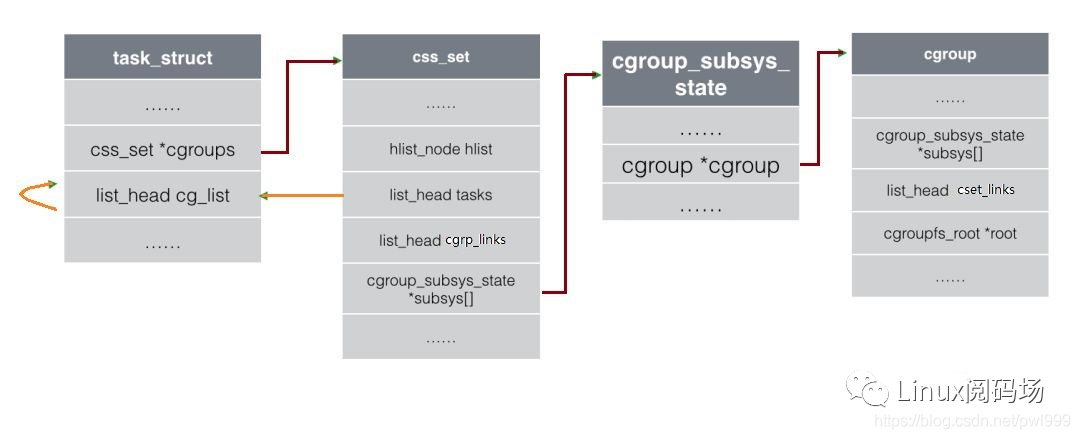
路径:task_struct->cgroup → css_set->subsys[] → cgroup_subsys_state->cgroup → cgroup
1.2、代码分析
1、"/proc/cgroups"
subsys的链表:for_each_subsys(ss, i)
一个susbsys对应一个hierarchy:ss->root
一个hierarchy有多少个cgroup:ss->root->nr_cgrps
# ount -t cgroup -o freezer,debug bbb freezer_test/# cat /proc/cgroups#subsys_name hierarchy num_cgroups enabledcpuset 4 6 1cpu 3 2 1cpuacct 1 147 1schedtune 2 3 1freezer 6 1 1debug 6 1 1
static int proc_cgroupstats_show(struct seq_file *m, void *v){struct cgroup_subsys *ss;int i;seq_puts(m, "#subsys_name hierarchy num_cgroups enabled ");/** ideally we don't want subsystems moving around while we do this.* cgroup_mutex is also necessary to guarantee an atomic snapshot of* subsys/hierarchy state.*/mutex_lock(&cgroup_mutex);for_each_subsys(ss, i)seq_printf(m, "%s %d %d %d ",ss->legacy_name, ss->root->hierarchy_id,atomic_read(&ss->root->nr_cgrps),cgroup_ssid_enabled(i));mutex_unlock(&cgroup_mutex);return 0;}
2、"/proc/pid/cgroup"
每种subsys组合组成一个新的hierarchy,每个hierarchy在for_each_root(root)中创建一个root树;
每个hierarchy顶层目录和子目录都是一个cgroup,一个hierarchy可以有多个cgroup,对应的subsys组合一样,但是参数不一样
cgroup_root自带一个cgroup即root->cgrp,作为hierarchy的顶级目录
一个cgroup对应多个subsys,使用cgroup_subsys_state类型(css)的cgroup->subsys[CGROUP_SUBSYS_COUNT]数组去和多个subsys链接;
一个cgroup自带一个cgroup_subsys_state即cgrp->self,这个css的作用是css->parent指针,建立起cgroup之间的父子关系;
css一个公用结构,每个subsys使用自己的函数ss->css_alloc()分配自己的css结构,这个结构包含公用css + subsys私有数据;
每个subsys只能存在于一个组合(hierarchy)当中,如果一个subsys已经被一个组合引用,其他组合不能再引用这个subsys。唯一例外的是,我们可以重复mount相同的组合,但是这样并没有创建新组合,只是创建了一个链接指向旧组合;
进程对应每一种hierarchy,一定有一个cgroup对应。
# cat /proc/832/cgroup6:freezer,debug:/4:cpuset:/3:cpu:/2:schedtune:/1:cpuacct:/
int proc_cgroup_show(struct seq_file *m, struct pid_namespace *ns,struct pid *pid, struct task_struct *tsk){char *buf, *path;int retval;struct cgroup_root *root;retval = -ENOMEM;buf = kmalloc(PATH_MAX, GFP_KERNEL);if (!buf)goto out;mutex_lock(&cgroup_mutex);spin_lock_bh(&css_set_lock);for_each_root(root) {struct cgroup_subsys *ss;struct cgroup *cgrp;int ssid, count = 0;if (root == &cgrp_dfl_root && !cgrp_dfl_root_visible)continue;seq_printf(m, "%d:", root->hierarchy_id);if (root != &cgrp_dfl_root)for_each_subsys(ss, ssid)if (root->subsys_mask & (1 << ssid))seq_printf(m, "%s%s", count++ ? "," : "",ss->legacy_name);if (strlen(root->name))seq_printf(m, "%sname=%s", count ? "," : "",root->name);seq_putc(m, ':');cgrp = task_cgroup_from_root(tsk, root);/** On traditional hierarchies, all zombie tasks show up as* belonging to the root cgroup. On the default hierarchy,* while a zombie doesn't show up in "cgroup.procs" and* thus can't be migrated, its /proc/PID/cgroup keeps* reporting the cgroup it belonged to before exiting. If* the cgroup is removed before the zombie is reaped,* " (deleted)" is appended to the cgroup path.*/if (cgroup_on_dfl(cgrp) || !(tsk->flags & PF_EXITING)) {path = cgroup_path(cgrp, buf, PATH_MAX);if (!path) {retval = -ENAMETOOLONG;goto out_unlock;}} else {path = "/";}seq_puts(m, path);if (cgroup_on_dfl(cgrp) && cgroup_is_dead(cgrp))seq_puts(m, " (deleted) ");elseseq_putc(m, ' ');}retval = 0;out_unlock:spin_unlock_bh(&css_set_lock);mutex_unlock(&cgroup_mutex);kfree(buf);out:return retval;}
3、初始化
int __init cgroup_init_early(void){static struct cgroup_sb_opts __initdata opts;struct cgroup_subsys *ss;int i;/* (1) 初始化默认root cgrp_dfl_root,选项opts为空,初始了root->cgrp // cgrp->root = root;root->cgrp.self // cgrp->self.cgroup = cgrp; cgrp->self.flags |= CSS_ONLINE;*/init_cgroup_root(&cgrp_dfl_root, &opts);cgrp_dfl_root.cgrp.self.flags |= CSS_NO_REF;RCU_INIT_POINTER(init_task.cgroups, &init_css_set);/* (2) 轮询subsys进行初始化 */for_each_subsys(ss, i) {WARN(!ss->css_alloc || !ss->css_free || ss->name || ss->id,"invalid cgroup_subsys %d:%s css_alloc=%p css_free=%p name:id=%d:%s ",i, cgroup_subsys_name[i], ss->css_alloc, ss->css_free,ss->id, ss->name);WARN(strlen(cgroup_subsys_name[i]) > MAX_CGROUP_TYPE_NAMELEN,"cgroup_subsys_name %s too long ", cgroup_subsys_name[i]);/* (3) 初始化ss->id、ss->name */ss->id = i;ss->name = cgroup_subsys_name[i];if (!ss->legacy_name)ss->legacy_name = cgroup_subsys_name[i];/* (4) ss链接到默认root(cgrp_dfl_root)默认css_set(init_css_set)指向ss*/if (ss->early_init)cgroup_init_subsys(ss, true);}return 0;}|→static void __init cgroup_init_subsys(struct cgroup_subsys *ss, bool early){struct cgroup_subsys_state *css;printk(KERN_INFO "Initializing cgroup subsys %s ", ss->name);mutex_lock(&cgroup_mutex);idr_init(&ss->css_idr);INIT_LIST_HEAD(&ss->cfts);/* Create the root cgroup state for this subsystem */ss->root = &cgrp_dfl_root;/* (4.1) subsys分配一个新的相关的cgroup_subsys_state */css = ss->css_alloc(cgroup_css(&cgrp_dfl_root.cgrp, ss));/* We don't handle early failures gracefully */BUG_ON(IS_ERR(css));/* (4.2) 初始化css的成员指向cgroupcgroup为默认值cgrp_dfl_root.cgrp:css->cgroup = cgrp;css->ss = ss;INIT_LIST_HEAD(&css->sibling);INIT_LIST_HEAD(&css->children);*/init_and_link_css(css, ss, &cgrp_dfl_root.cgrp);/** Root csses are never destroyed and we can't initialize* percpu_ref during early init. Disable refcnting.*/css->flags |= CSS_NO_REF;if (early) {/* allocation can't be done safely during early init */css->id = 1;} else {css->id = cgroup_idr_alloc(&ss->css_idr, css, 1, 2, GFP_KERNEL);BUG_ON(css->id < 0);}/* Update the init_css_set to contain a subsys* pointer to this state - since the subsystem is* newly registered, all tasks and hence the* init_css_set is in the subsystem's root cgroup. *//* (4.3) css_set指向新的css */init_css_set.subsys[ss->id] = css;have_fork_callback |= (bool)ss->fork << ss->id;have_exit_callback |= (bool)ss->exit << ss->id;have_free_callback |= (bool)ss->free << ss->id;have_canfork_callback |= (bool)ss->can_fork << ss->id;/* At system boot, before all subsystems have been* registered, no tasks have been forked, so we don't* need to invoke fork callbacks here. */BUG_ON(!list_empty(&init_task.tasks));/* (4.4) cgroup测指向css:执行ss->css_online(css);css->cgroup->subsys[ss->id] = css;*/BUG_ON(online_css(css));mutex_unlock(&cgroup_mutex);}int __init cgroup_init(void){struct cgroup_subsys *ss;int ssid;BUG_ON(percpu_init_rwsem(&cgroup_threadgroup_rwsem));BUG_ON(cgroup_init_cftypes(NULL, cgroup_dfl_base_files));BUG_ON(cgroup_init_cftypes(NULL, cgroup_legacy_base_files));/** The latency of the synchronize_sched() is too high for cgroups,* avoid it at the cost of forcing all readers into the slow path.*/rcu_sync_enter_start(&cgroup_threadgroup_rwsem.rss);mutex_lock(&cgroup_mutex);/** Add init_css_set to the hash table so that dfl_root can link to* it during init.*/hash_add(css_set_table, &init_css_set.hlist,css_set_hash(init_css_set.subsys));BUG_ON(cgroup_setup_root(&cgrp_dfl_root, 0));mutex_unlock(&cgroup_mutex);for_each_subsys(ss, ssid) {if (ss->early_init) {struct cgroup_subsys_state *css =init_css_set.subsys[ss->id];css->id = cgroup_idr_alloc(&ss->css_idr, css, 1, 2,GFP_KERNEL);BUG_ON(css->id < 0);} else {cgroup_init_subsys(ss, false);}list_add_tail(&init_css_set.e_cset_node[ssid],&cgrp_dfl_root.cgrp.e_csets[ssid]);/** Setting dfl_root subsys_mask needs to consider the* disabled flag and cftype registration needs kmalloc,* both of which aren't available during early_init.*/if (cgroup_disable_mask & (1 << ssid)) {static_branch_disable(cgroup_subsys_enabled_key[ssid]);printk(KERN_INFO "Disabling %s control group subsystem ",ss->name);continue;}/* (1) 默认root(cgrp_dfl_root),支持所有ss */cgrp_dfl_root.subsys_mask |= 1 << ss->id;if (!ss->dfl_cftypes)cgrp_dfl_root_inhibit_ss_mask |= 1 << ss->id;/* (2) 将cftypes(ss->legacy_cftypes/ss->legacy_cftypes)加入到ss->cfts链表 */if (ss->dfl_cftypes == ss->legacy_cftypes) {WARN_ON(cgroup_add_cftypes(ss, ss->dfl_cftypes));} else {WARN_ON(cgroup_add_dfl_cftypes(ss, ss->dfl_cftypes));WARN_ON(cgroup_add_legacy_cftypes(ss, ss->legacy_cftypes));}if (ss->bind)ss->bind(init_css_set.subsys[ssid]);}/* init_css_set.subsys[] has been updated, re-hash */hash_del(&init_css_set.hlist);hash_add(css_set_table, &init_css_set.hlist,css_set_hash(init_css_set.subsys));WARN_ON(sysfs_create_mount_point(fs_kobj, "cgroup"));WARN_ON(register_filesystem(&cgroup_fs_type));WARN_ON(!proc_create("cgroups", 0, NULL, &proc_cgroupstats_operations));return 0;}
4、mount操作
创建新的root,因为ss默认都和默认root(cgrp_dfl_root)建立了关系,所以ss需要先解除旧的root链接,再和新root建立起链接。
static struct dentry *cgroup_mount(struct file_system_type *fs_type,int flags, const char *unused_dev_name,void *data){struct super_block *pinned_sb = NULL;struct cgroup_subsys *ss;struct cgroup_root *root;struct cgroup_sb_opts opts;struct dentry *dentry;int ret;int i;bool new_sb;/** The first time anyone tries to mount a cgroup, enable the list* linking each css_set to its tasks and fix up all existing tasks.*/if (!use_task_css_set_links)cgroup_enable_task_cg_lists();mutex_lock(&cgroup_mutex);/* First find the desired set of subsystems *//* (1) 解析mount选项到opts */ret = parse_cgroupfs_options(data, &opts);if (ret)goto out_unlock;/* look for a matching existing root */if (opts.flags & CGRP_ROOT_SANE_BEHAVIOR) {cgrp_dfl_root_visible = true;root = &cgrp_dfl_root;cgroup_get(&root->cgrp);ret = 0;goto out_unlock;}/** Destruction of cgroup root is asynchronous, so subsystems may* still be dying after the previous unmount. Let's drain the* dying subsystems. We just need to ensure that the ones* unmounted previously finish dying and don't care about new ones* starting. Testing ref liveliness is good enough.*//* (2) */for_each_subsys(ss, i) {if (!(opts.subsys_mask & (1 << i)) ||ss->root == &cgrp_dfl_root)continue;if (!percpu_ref_tryget_live(&ss->root->cgrp.self.refcnt)) {mutex_unlock(&cgroup_mutex);msleep(10);ret = restart_syscall();goto out_free;}cgroup_put(&ss->root->cgrp);}/* (3) */for_each_root(root) {bool name_match = false;if (root == &cgrp_dfl_root)continue;/** If we asked for a name then it must match. Also, if* name matches but sybsys_mask doesn't, we should fail.* Remember whether name matched.*/if (opts.name) {if (strcmp(opts.name, root->name))continue;name_match = true;}/** If we asked for subsystems (or explicitly for no* subsystems) then they must match.*/if ((opts.subsys_mask || opts.none) &&(opts.subsys_mask != root->subsys_mask)) {if (!name_match)continue;ret = -EBUSY;goto out_unlock;}if (root->flags ^ opts.flags)pr_warn("new mount options do not match the existing superblock, will be ignored ");/** We want to reuse @root whose lifetime is governed by its* ->cgrp. Let's check whether @root is alive and keep it* that way. As cgroup_kill_sb() can happen anytime, we* want to block it by pinning the sb so that @root doesn't* get killed before mount is complete.** With the sb pinned, tryget_live can reliably indicate* whether @root can be reused. If it's being killed,* drain it. We can use wait_queue for the wait but this* path is super cold. Let's just sleep a bit and retry.*/pinned_sb = kernfs_pin_sb(root->kf_root, NULL);if (IS_ERR(pinned_sb) ||!percpu_ref_tryget_live(&root->cgrp.self.refcnt)) {mutex_unlock(&cgroup_mutex);if (!IS_ERR_OR_NULL(pinned_sb))deactivate_super(pinned_sb);msleep(10);ret = restart_syscall();goto out_free;}ret = 0;goto out_unlock;}/** No such thing, create a new one. name= matching without subsys* specification is allowed for already existing hierarchies but we* can't create new one without subsys specification.*/if (!opts.subsys_mask && !opts.none) {ret = -EINVAL;goto out_unlock;}/* (4) 分配新的root */root = kzalloc(sizeof(*root), GFP_KERNEL);if (!root) {ret = -ENOMEM;goto out_unlock;}/* (5) 初始化新的root,初始了root->cgrp // cgrp->root = root;root->cgrp.self // cgrp->self.cgroup = cgrp; cgrp->self.flags |= CSS_ONLINE;root->name = opts->name*/init_cgroup_root(root, &opts);/* (6) 将新的root和opts.subsys_mask指向的多个ss进行链接 */ret = cgroup_setup_root(root, opts.subsys_mask);if (ret)cgroup_free_root(root);out_unlock:mutex_unlock(&cgroup_mutex);out_free:kfree(opts.release_agent);kfree(opts.name);if (ret)return ERR_PTR(ret);/* (7) mount新root对应的根目录 */dentry = kernfs_mount(fs_type, flags, root->kf_root,CGROUP_SUPER_MAGIC, &new_sb);if (IS_ERR(dentry) || !new_sb)cgroup_put(&root->cgrp);/** If @pinned_sb, we're reusing an existing root and holding an* extra ref on its sb. Mount is complete. Put the extra ref.*/if (pinned_sb) {WARN_ON(new_sb);deactivate_super(pinned_sb);}return dentry;}|→static int cgroup_setup_root(struct cgroup_root *root, unsigned long ss_mask){LIST_HEAD(tmp_links);struct cgroup *root_cgrp = &root->cgrp;struct css_set *cset;int i, ret;lockdep_assert_held(&cgroup_mutex);ret = cgroup_idr_alloc(&root->cgroup_idr, root_cgrp, 1, 2, GFP_KERNEL);if (ret < 0)goto out;root_cgrp->id = ret;ret = percpu_ref_init(&root_cgrp->self.refcnt, css_release, 0,GFP_KERNEL);if (ret)goto out;/** We're accessing css_set_count without locking css_set_lock here,* but that's OK - it can only be increased by someone holding* cgroup_lock, and that's us. The worst that can happen is that we* have some link structures left over*/ret = allocate_cgrp_cset_links(css_set_count, &tmp_links);if (ret)goto cancel_ref;ret = cgroup_init_root_id(root);if (ret)goto cancel_ref;/* (6.1) 创建root对应的顶层root文件夹 */root->kf_root = kernfs_create_root(&cgroup_kf_syscall_ops,KERNFS_ROOT_CREATE_DEACTIVATED,root_cgrp);if (IS_ERR(root->kf_root)) {ret = PTR_ERR(root->kf_root);goto exit_root_id;}root_cgrp->kn = root->kf_root->kn;/* (6.2) 创建cgroup自己对应的一些file,cgroup自己的file由cgroup自己的css(cgrp->self)承担,后面cgroup会依次创建每个subsys的file,subsys的file由每个ss对应的css(cgrp->subsys[])承担*/ret = css_populate_dir(&root_cgrp->self, NULL);if (ret)goto destroy_root;/* (6.3) 将新root需要的subsys和原默认root(cgrp_dfl_root)解除关系,并且把这些ss重新和新root建立关系*/ret = rebind_subsystems(root, ss_mask);if (ret)goto destroy_root;/** There must be no failure case after here, since rebinding takes* care of subsystems' refcounts, which are explicitly dropped in* the failure exit path.*/list_add(&root->root_list, &cgroup_roots);cgroup_root_count++;/** Link the root cgroup in this hierarchy into all the css_set* objects.*/spin_lock_bh(&css_set_lock);hash_for_each(css_set_table, i, cset, hlist) {link_css_set(&tmp_links, cset, root_cgrp);if (css_set_populated(cset))cgroup_update_populated(root_cgrp, true);}spin_unlock_bh(&css_set_lock);BUG_ON(!list_empty(&root_cgrp->self.children));BUG_ON(atomic_read(&root->nr_cgrps) != 1);kernfs_activate(root_cgrp->kn);ret = 0;goto out;destroy_root:kernfs_destroy_root(root->kf_root);root->kf_root = NULL;exit_root_id:cgroup_exit_root_id(root);cancel_ref:percpu_ref_exit(&root_cgrp->self.refcnt);out:free_cgrp_cset_links(&tmp_links);return ret;}||→static int rebind_subsystems(struct cgroup_root *dst_root,unsigned long ss_mask){struct cgroup *dcgrp = &dst_root->cgrp;struct cgroup_subsys *ss;unsigned long tmp_ss_mask;int ssid, i, ret;lockdep_assert_held(&cgroup_mutex);for_each_subsys_which(ss, ssid, &ss_mask) {/* if @ss has non-root csses attached to it, can't move */if (css_next_child(NULL, cgroup_css(&ss->root->cgrp, ss)))return -EBUSY;/* can't move between two non-dummy roots either */if (ss->root != &cgrp_dfl_root && dst_root != &cgrp_dfl_root)return -EBUSY;}/* skip creating root files on dfl_root for inhibited subsystems */tmp_ss_mask = ss_mask;if (dst_root == &cgrp_dfl_root)tmp_ss_mask &= ~cgrp_dfl_root_inhibit_ss_mask;for_each_subsys_which(ss, ssid, &tmp_ss_mask) {struct cgroup *scgrp = &ss->root->cgrp;int tssid;/* (6.3.1) 在新root的根cgroup(dst_root->cgrp)下,根据subsys的file链表(css->ss->cfts)创建subsys对应的file*/ret = css_populate_dir(cgroup_css(scgrp, ss), dcgrp);if (!ret)continue;/** Rebinding back to the default root is not allowed to* fail. Using both default and non-default roots should* be rare. Moving subsystems back and forth even more so.* Just warn about it and continue.*/if (dst_root == &cgrp_dfl_root) {if (cgrp_dfl_root_visible) {pr_warn("failed to create files (%d) while rebinding 0x%lx to default root ",ret, ss_mask);pr_warn("you may retry by moving them to a different hierarchy and unbinding ");}continue;}for_each_subsys_which(ss, tssid, &tmp_ss_mask) {if (tssid == ssid)break;css_clear_dir(cgroup_css(scgrp, ss), dcgrp);}return ret;}/** Nothing can fail from this point on. Remove files for the* removed subsystems and rebind each subsystem.*/for_each_subsys_which(ss, ssid, &ss_mask) {struct cgroup_root *src_root = ss->root;struct cgroup *scgrp = &src_root->cgrp;struct cgroup_subsys_state *css = cgroup_css(scgrp, ss);struct css_set *cset;WARN_ON(!css || cgroup_css(dcgrp, ss));css_clear_dir(css, NULL);/* (6.3.2) 取消原root cgroup对subsys的css的引用 */RCU_INIT_POINTER(scgrp->subsys[ssid], NULL);/* (6.3.3) 链接新root cgroup和subsys的css的引用 */rcu_assign_pointer(dcgrp->subsys[ssid], css);ss->root = dst_root;css->cgroup = dcgrp;spin_lock_bh(&css_set_lock);hash_for_each(css_set_table, i, cset, hlist)list_move_tail(&cset->e_cset_node[ss->id],&dcgrp->e_csets[ss->id]);spin_unlock_bh(&css_set_lock);src_root->subsys_mask &= ~(1 << ssid);scgrp->subtree_control &= ~(1 << ssid);cgroup_refresh_child_subsys_mask(scgrp);/* default hierarchy doesn't enable controllers by default */dst_root->subsys_mask |= 1 << ssid;if (dst_root == &cgrp_dfl_root) {static_branch_enable(cgroup_subsys_on_dfl_key[ssid]);} else {dcgrp->subtree_control |= 1 << ssid;cgroup_refresh_child_subsys_mask(dcgrp);static_branch_disable(cgroup_subsys_on_dfl_key[ssid]);}if (ss->bind)ss->bind(css);}kernfs_activate(dcgrp->kn);return 0;}
5、文件操作
创建一个新文件夹,相当于创建一个新的cgroup。我们重点来看看新建文件夹的操作:
static struct kernfs_syscall_ops cgroup_kf_syscall_ops = {.remount_fs = cgroup_remount,.show_options = cgroup_show_options,.mkdir = cgroup_mkdir,.rmdir = cgroup_rmdir,.rename = cgroup_rename,};static int cgroup_mkdir(struct kernfs_node *parent_kn, const char *name,umode_t mode){struct cgroup *parent, *cgrp;struct cgroup_root *root;struct cgroup_subsys *ss;struct kernfs_node *kn;int ssid, ret;/* Do not accept ' ' to prevent making /proc//cgroup unparsable. */if (strchr(name, ' '))return -EINVAL;parent = cgroup_kn_lock_live(parent_kn);if (!parent)return -ENODEV;root = parent->root;/* allocate the cgroup and its ID, 0 is reserved for the root *//* (1) 分配新的cgroup */cgrp = kzalloc(sizeof(*cgrp), GFP_KERNEL);if (!cgrp) {ret = -ENOMEM;goto out_unlock;}ret = percpu_ref_init(&cgrp->self.refcnt, css_release, 0, GFP_KERNEL);if (ret)goto out_free_cgrp;/** Temporarily set the pointer to NULL, so idr_find() won't return* a half-baked cgroup.*/cgrp->id = cgroup_idr_alloc(&root->cgroup_idr, NULL, 2, 0, GFP_KERNEL);if (cgrp->id < 0) {ret = -ENOMEM;goto out_cancel_ref;}/* (2) 初始化cgroup */init_cgroup_housekeeping(cgrp);/* (3) 和父cgroup之间建立起关系 */cgrp->self.parent = &parent->self;cgrp->root = root;if (notify_on_release(parent))set_bit(CGRP_NOTIFY_ON_RELEASE, &cgrp->flags);if (test_bit(CGRP_CPUSET_CLONE_CHILDREN, &parent->flags))set_bit(CGRP_CPUSET_CLONE_CHILDREN, &cgrp->flags);/* create the directory *//* (3) 创建新的cgroup对应的文件夹 */kn = kernfs_create_dir(parent->kn, name, mode, cgrp);if (IS_ERR(kn)) {ret = PTR_ERR(kn);goto out_free_id;}cgrp->kn = kn;/** This extra ref will be put in cgroup_free_fn() and guarantees* that @cgrp->kn is always accessible.*/kernfs_get(kn);cgrp->self.serial_nr = css_serial_nr_next++;/* allocation complete, commit to creation */list_add_tail_rcu(&cgrp->self.sibling, &cgroup_parent(cgrp)->self.children);atomic_inc(&root->nr_cgrps);cgroup_get(parent);/** @cgrp is now fully operational. If something fails after this* point, it'll be released via the normal destruction path.*/cgroup_idr_replace(&root->cgroup_idr, cgrp, cgrp->id);ret = cgroup_kn_set_ugid(kn);if (ret)goto out_destroy;/* (4) 新cgroup文件夹下创建cgroup自己css对应的默认file */ret = css_populate_dir(&cgrp->self, NULL);if (ret)goto out_destroy;/* let's create and online css's *//* (5) 针对root对应的各个susbsys, 每个subsys创建新的css并且在cgroup文件夹下创建css对应的file*/for_each_subsys(ss, ssid) {if (parent->child_subsys_mask & (1 << ssid)) {ret = create_css(cgrp, ss,parent->subtree_control & (1 << ssid));if (ret)goto out_destroy;}}/** On the default hierarchy, a child doesn't automatically inherit* subtree_control from the parent. Each is configured manually.*/if (!cgroup_on_dfl(cgrp)) {cgrp->subtree_control = parent->subtree_control;cgroup_refresh_child_subsys_mask(cgrp);}kernfs_activate(kn);ret = 0;goto out_unlock;out_free_id:cgroup_idr_remove(&root->cgroup_idr, cgrp->id);out_cancel_ref:percpu_ref_exit(&cgrp->self.refcnt);out_free_cgrp:kfree(cgrp);out_unlock:cgroup_kn_unlock(parent_kn);return ret;out_destroy:cgroup_destroy_locked(cgrp);goto out_unlock;}
cgroup默认文件,有一些重要的文件比如“tasks”,我们来看看具体的操作。
static struct cftype cgroup_legacy_base_files[] = {{.name = "cgroup.procs",.seq_start = cgroup_pidlist_start,.seq_next = cgroup_pidlist_next,.seq_stop = cgroup_pidlist_stop,.seq_show = cgroup_pidlist_show,.private = CGROUP_FILE_PROCS,.write = cgroup_procs_write,},{.name = "cgroup.clone_children",.read_u64 = cgroup_clone_children_read,.write_u64 = cgroup_clone_children_write,},{.name = "cgroup.sane_behavior",.flags = CFTYPE_ONLY_ON_ROOT,.seq_show = cgroup_sane_behavior_show,},{.name = "tasks",.seq_start = cgroup_pidlist_start,.seq_next = cgroup_pidlist_next,.seq_stop = cgroup_pidlist_stop,.seq_show = cgroup_pidlist_show,.private = CGROUP_FILE_TASKS,.write = cgroup_tasks_write,},{.name = "notify_on_release",.read_u64 = cgroup_read_notify_on_release,.write_u64 = cgroup_write_notify_on_release,},{.name = "release_agent",.flags = CFTYPE_ONLY_ON_ROOT,.seq_show = cgroup_release_agent_show,.write = cgroup_release_agent_write,.max_write_len = PATH_MAX - 1,},{ } /* terminate */}static ssize_t cgroup_tasks_write(struct kernfs_open_file *of,char *buf, size_t nbytes, loff_t off){return __cgroup_procs_write(of, buf, nbytes, off, false);}|→static ssize_t __cgroup_procs_write(struct kernfs_open_file *of, char *buf,size_t nbytes, loff_t off, bool threadgroup){struct task_struct *tsk;struct cgroup_subsys *ss;struct cgroup *cgrp;pid_t pid;int ssid, ret;if (kstrtoint(strstrip(buf), 0, &pid) || pid < 0)return -EINVAL;cgrp = cgroup_kn_lock_live(of->kn);if (!cgrp)return -ENODEV;percpu_down_write(&cgroup_threadgroup_rwsem);rcu_read_lock();if (pid) {tsk = find_task_by_vpid(pid);if (!tsk) {ret = -ESRCH;goto out_unlock_rcu;}} else {tsk = current;}if (threadgroup)tsk = tsk->group_leader;/** Workqueue threads may acquire PF_NO_SETAFFINITY and become* trapped in a cpuset, or RT worker may be born in a cgroup* with no rt_runtime allocated. Just say no.*/if (tsk == kthreadd_task || (tsk->flags & PF_NO_SETAFFINITY)) {ret = -EINVAL;goto out_unlock_rcu;}get_task_struct(tsk);rcu_read_unlock();ret = cgroup_procs_write_permission(tsk, cgrp, of);if (!ret) {/* (1) attach task到cgroup */ret = cgroup_attach_task(cgrp, tsk, threadgroup);if (cgrp->id != SS_TOP_GROUP_ID && cgrp->child_subsys_mask == CSS_CPUSET_MASK&& excl_task_count > 0) {remove_set_exclusive_task(tsk->pid, 0);}}put_task_struct(tsk);goto out_unlock_threadgroup;out_unlock_rcu:rcu_read_unlock();out_unlock_threadgroup:percpu_up_write(&cgroup_threadgroup_rwsem);for_each_subsys(ss, ssid)if (ss->post_attach)ss->post_attach();cgroup_kn_unlock(of->kn);return ret ?: nbytes;}||→static int cgroup_attach_task(struct cgroup *dst_cgrp,struct task_struct *leader, bool threadgroup){LIST_HEAD(preloaded_csets);struct task_struct *task;int ret;/* look up all src csets */spin_lock_bh(&css_set_lock);rcu_read_lock();task = leader;/* (1.1) 遍历task所在线程组,把需要迁移的进程的css_set加入到preloaded_csets链表 */do {cgroup_migrate_add_src(task_css_set(task), dst_cgrp,&preloaded_csets);if (!threadgroup)break;} while_each_thread(leader, task);rcu_read_unlock();spin_unlock_bh(&css_set_lock);/* (1.2) 去掉旧的css_set对css的应用,分配新的css_set承担新的css组合的应用,并且给进程使用*//* prepare dst csets and commit */ret = cgroup_migrate_prepare_dst(dst_cgrp, &preloaded_csets);if (!ret)ret = cgroup_migrate(leader, threadgroup, dst_cgrp);cgroup_migrate_finish(&preloaded_csets);return ret;}
1.3、cgroup subsystem
我们关注cgroup子系统具体能提供的功能。
1.3.1、cpu
kernel/sched/core.c。会创建新的task_group,可以对cgroup对应的task_group进行cfs/rt类型的带宽控制。
static struct cftype cpu_files[] = {{.name = "shares",.read_u64 = cpu_shares_read_u64,.write_u64 = cpu_shares_write_u64,},{.name = "cfs_quota_us",.read_s64 = cpu_cfs_quota_read_s64,.write_s64 = cpu_cfs_quota_write_s64,},{.name = "cfs_period_us",.read_u64 = cpu_cfs_period_read_u64,.write_u64 = cpu_cfs_period_write_u64,},{.name = "stat",.seq_show = cpu_stats_show,},{.name = "rt_runtime_us",.read_s64 = cpu_rt_runtime_read,.write_s64 = cpu_rt_runtime_write,},{.name = "rt_period_us",.read_u64 = cpu_rt_period_read_uint,.write_u64 = cpu_rt_period_write_uint,},{ } /* terminate */};struct cgroup_subsys cpu_cgrp_subsys = {.css_alloc = cpu_cgroup_css_alloc, // 分配新的task_group.css_released = cpu_cgroup_css_released,.css_free = cpu_cgroup_css_free,.fork = cpu_cgroup_fork,.can_attach = cpu_cgroup_can_attach,.attach = cpu_cgroup_attach,.legacy_cftypes = cpu_files,.early_init = 1,};
1.3.2、cpuset
kernel/cpusec.c。给cgroup分配不同的cpu和mem node节点,还可以配置一些flag。
static struct cftype files[] = {{.name = "cpus",.seq_show = cpuset_common_seq_show,.write = cpuset_write_resmask,.max_write_len = (100U + 6 * NR_CPUS),.private = FILE_CPULIST,},{.name = "mems",.seq_show = cpuset_common_seq_show,.write = cpuset_write_resmask,.max_write_len = (100U + 6 * MAX_NUMNODES),.private = FILE_MEMLIST,},{.name = "effective_cpus",.seq_show = cpuset_common_seq_show,.private = FILE_EFFECTIVE_CPULIST,},{.name = "effective_mems",.seq_show = cpuset_common_seq_show,.private = FILE_EFFECTIVE_MEMLIST,},{.name = "cpu_exclusive",.read_u64 = cpuset_read_u64,.write_u64 = cpuset_write_u64,.private = FILE_CPU_EXCLUSIVE,},{.name = "mem_exclusive",.read_u64 = cpuset_read_u64,.write_u64 = cpuset_write_u64,.private = FILE_MEM_EXCLUSIVE,},{.name = "mem_hardwall",.read_u64 = cpuset_read_u64,.write_u64 = cpuset_write_u64,.private = FILE_MEM_HARDWALL,},{.name = "sched_load_balance",.read_u64 = cpuset_read_u64,.write_u64 = cpuset_write_u64,.private = FILE_SCHED_LOAD_BALANCE,},{.name = "sched_relax_domain_level",.read_s64 = cpuset_read_s64,.write_s64 = cpuset_write_s64,.private = FILE_SCHED_RELAX_DOMAIN_LEVEL,},{.name = "memory_migrate",.read_u64 = cpuset_read_u64,.write_u64 = cpuset_write_u64,.private = FILE_MEMORY_MIGRATE,},{.name = "memory_pressure",.read_u64 = cpuset_read_u64,},{.name = "memory_spread_page",.read_u64 = cpuset_read_u64,.write_u64 = cpuset_write_u64,.private = FILE_SPREAD_PAGE,},{.name = "memory_spread_slab",.read_u64 = cpuset_read_u64,.write_u64 = cpuset_write_u64,.private = FILE_SPREAD_SLAB,},{.name = "memory_pressure_enabled",.flags = CFTYPE_ONLY_ON_ROOT,.read_u64 = cpuset_read_u64,.write_u64 = cpuset_write_u64,.private = FILE_MEMORY_PRESSURE_ENABLED,},{ } /* terminate */}struct cgroup_subsys cpuset_cgrp_subsys = {.css_alloc = cpuset_css_alloc,.css_online = cpuset_css_online,.css_offline = cpuset_css_offline,.css_free = cpuset_css_free,.can_attach = cpuset_can_attach,.cancel_attach = cpuset_cancel_attach,.attach = cpuset_attach,.post_attach = cpuset_post_attach,.bind = cpuset_bind,.fork = cpuset_fork,.legacy_cftypes = files,.early_init = 1,};
1.3.3、schedtune
kernel/sched/tune.c,可以进行schedle boost操作。
static struct cftype files[] = {{.name = "boost",.read_u64 = boost_read,.write_u64 = boost_write,},{.name = "prefer_idle",.read_u64 = prefer_idle_read,.write_u64 = prefer_idle_write,},{ } /* terminate */};struct cgroup_subsys schedtune_cgrp_subsys = {.css_alloc = schedtune_css_alloc,.css_free = schedtune_css_free,.legacy_cftypes = files,.early_init = 1,};
1.3.4、cpuacct
kernel/sched/cpuacct.c,可以按照cgroup的分组来统计cpu占用率。
static struct cftype files[] = {{.name = "usage",.read_u64 = cpuusage_read,.write_u64 = cpuusage_write,},{.name = "usage_percpu",.seq_show = cpuacct_percpu_seq_show,},{.name = "stat",.seq_show = cpuacct_stats_show,},{ } /* terminate */};struct cgroup_subsys cpuacct_cgrp_subsys = {.css_alloc = cpuacct_css_alloc,.css_free = cpuacct_css_free,.legacy_cftypes = files,.early_init = 1,};
原文标题:Linux schedule 之 Cgroup
文章出处:【微信公众号:Linux阅码场】欢迎添加关注!文章转载请注明出处。
-
Linux
+关注
关注
88文章
11628浏览量
217973 -
数据结构
+关注
关注
3文章
573浏览量
41373 -
文件夹
+关注
关注
0文章
14浏览量
8510
原文标题:Linux schedule 之 Cgroup
文章出处:【微信号:LinuxDev,微信公众号:Linux阅码场】欢迎添加关注!文章转载请注明出处。
发布评论请先 登录
一文详细了解JTAG接口
一文了解MyBatis的查询原理
用VDK+BF537开发产品中,想详细了解一下VDK中事件、事件bit、信号量的使用方法,以及如何写自己的device drivers
详细了解下ups的相关计算
详细了解一下STM32F1的具体电路参数
一文详细了解HarmonyOS工程
一文详细了解OpenHarmony新图形框架
一文详细了解CCIX规范
如何在Kubernetes中快速启用Cgroup V2支持
带您一起详细了解IEEE802.3bt(PoE++)的有关特点





 一文详细了解Cgroup
一文详细了解Cgroup












评论